CPS 230 is ushering in a new era for operational risk management among Australian financial services institutions. A key component of the new standard focuses on the effective management of critical operations which are essential for seamless operations, delivery of services to customers and the stability of the financial industry as a whole. In this article, we will clarify the concept of critical operations under CPS 230, as well as providing some guidance on tricky issues to address.
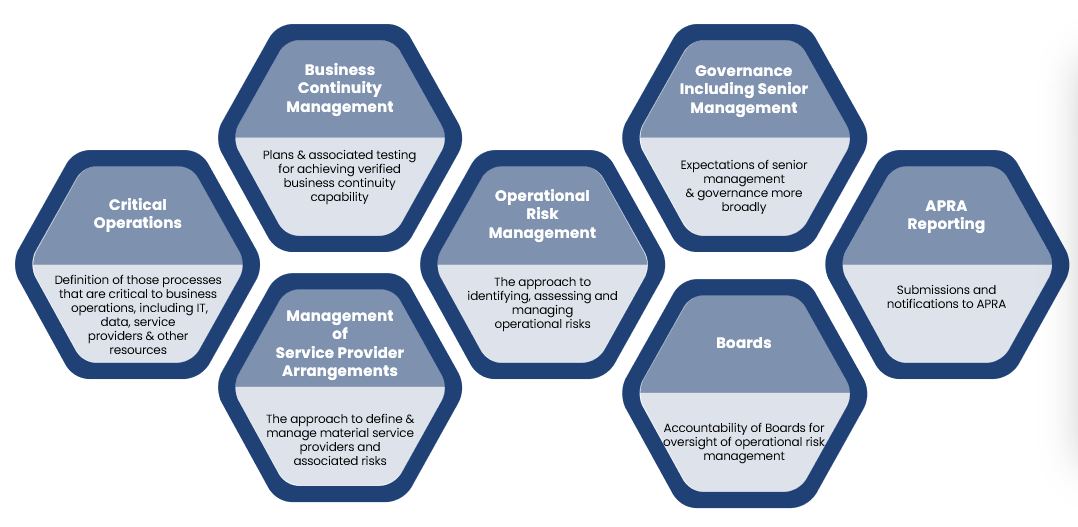
This article builds on the 7 Domains of Compliance for CPS 230 outlined below that we have outlined in our previous blog post.
Understanding your critical operations is a significant first step
APRA has been clear on their expectations as entities transition to CPS 230 compliance:
“mapping out critical operations and identifying material service providers is a practical initial step, as is building organisational awareness…” APRA Chair John Lonsdale (Speech to FINSIA The Regulators, Nov 2023).
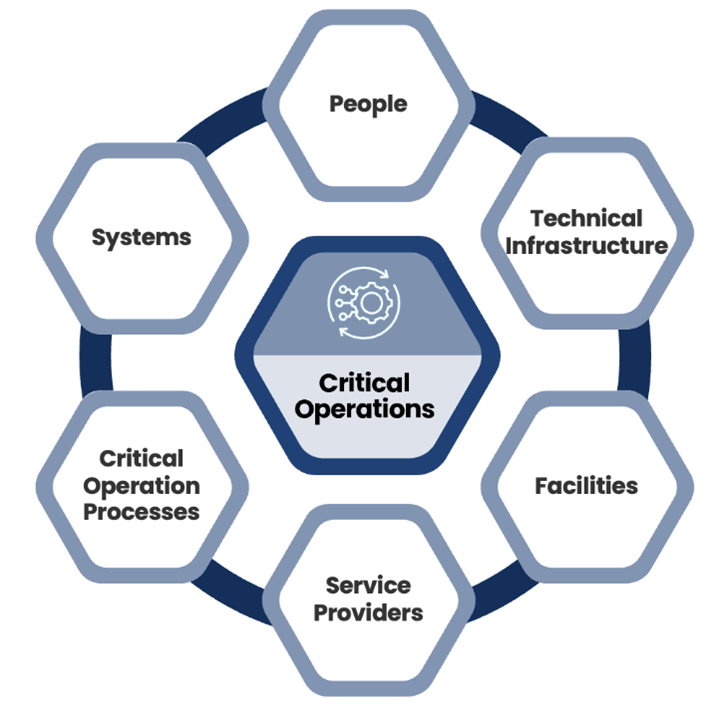
In readiness for CPS 230, APRA-regulated entities must define, identify and maintain a register of critical operations. Entities must also document the necessary processes and resources needed to deliver these operations. This includes:
- people especially single point sensitivities
- technology focussing on key risks such as end of life assets
- information including key data linkages
- facilities whether on site or offsite
- service providers especially those identified historically as ‘outsource arrangements’
- any key obligations
- interdependencies between any of the above
These data points will enable risks, controls and areas of weakness to be identified and therefore reported and managed. Getting this right is foundational to meeting the broader requirements of CPS 230.
So what are Critical Operations in the context of CPS 230?
These are defined as “processes undertaken by an APRA-regulated entity or its service provider which, if disrupted beyond tolerance levels, would have a material adverse impact on its depositors, policyholders, beneficiaries or other customers, or its role in the financial system”. The standard identifies common critical operations, summarised below, (but does not provide an exhaustive list):
- ADIs: Payments, Deposit-Taking, and Management, Custody, Settlements and Clearing
- Insurers: Claims Processing
- RSE Licensees: Investment Management and Fund Administration
- All APRA-regulated entities: Customer Enquiries and the Systems and Infrastructure needed to support critical operations
Unsurprisingly, key requirements on FSIs for critical operations include the need to maintain critical operations within tolerance levels through severe disruptions, prevent disruptions to critical operations and return promptly to normal operations once a disruption is over.
What are the changes from the current regulations?
There is now a greater focus on operations that are customer facing or systemically important. This will necessitate a review by entities as to what they currently consider as critical operations.
CPS 230 also introduces a significant step change in the level of rigour and detail previously required under existing standards eg. Business Continuity CPS 232. FSIs must now document and maintain all processes and resources needed to deliver critical operations. This will require much more clarity of end-to-end business processes and the underlying supporting elements (as listed above) and documenting or systematising these.
APRA has also set expectations with respect to information and technology (which further builds on CPS 234) and now goes beyond information security to ensure their technology platforms remain ‘fit for purpose’. Increased organisational awareness must include building appropriate mechanisms to enable Board and senior management to effectively oversee the health, risks and weaknesses of the critical operations including information and technology.
Our observations on challenges facing FSIs
Capital Consult is working with a number of FSIs with CPS 230 readiness and we have observed a range of issues being faced. It is important to assess your organisation’s exposure to these challenges and determine a practical way forward :
- End-to-end process mapping – CPS 230 requires a more process-based and integrated view of critical business operations, rather than the previously primarily functional and infrastructure view. It may not be sufficient to simply enhance existing lists of critical assets previously used to inform Business Impact Assessments.
- Level of detail – The quantity of detail collected for critical operations requires pragmatism. Collect too little and the register of critical operations is unlikely to meet the intent of the new standard. Collect too much and you will have a serious management issue as you maintain the register currency and risk profiles going forward.
- Material vs Critical – The need to reassess the previous methodology to determine ‘material outsource arrangements’ (under CPS 231) and align to CPS 230 in determining critical service providers.
- It’s not just a new tool – There is a large array of vendors offering tools to capture and document critical operations. Many FSIs are unsure whether this is required or necessary or if their existing toolset for process mapping is adequate.
- Technology health – Rigour in maintaining a healthy technology landscape (including timely remediation of end-of-life issues, appropriate investment in support and systematically monitoring and measuring the health of technology platforms). APRA’s recent CPS 234 independent assessments have also identified a number of weaknesses with respect to CPS 234 requirements.
- Evidence of compliance – APRA has stated they will be assessing entities progress. Having an early and complete view of what evidence will be required for compliance and ongoing (across all 7 domains) assists planning, workload and deliverables expected.
More broadly, CPS 230 has also turned up the heat on work required with respect to operational risk management, business continuity, service provider management, and expectations of Board and senior management. These will be addressed in subsequent articles.
In Summary
With CPS 230 taking effect on 1 July 2025 FSIs do not have long. APRA has been clear that it expects to see progress well before then and a focus on critical operations is a good place to start. FSI’s must be able to demonstrate a well thought through plan towards compliance. The importance of understanding priority areas and developing a compliance roadmap early should not be underestimated.
The Capital Consult team is happy to help with advice and ideas on where we can assist with CPS 230 readiness so contact us.
About the Authors: Neo Aplin and Robin Wall are from Capital Consult, a specialist provider of advice, consulting, and services to the Financial Services industry since 2008. Capital Consult assists organizations in interpreting and achieving compliance with APRA prudential standards, guidelines, and supervisory directions. The authors have extensive experience in helping FSI clients manage their APRA and regulatory obligations including CPS 230 readiness.
